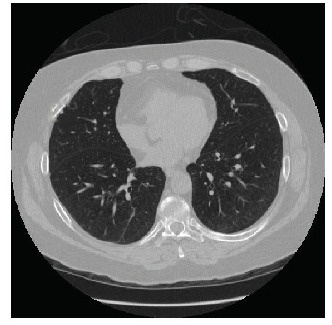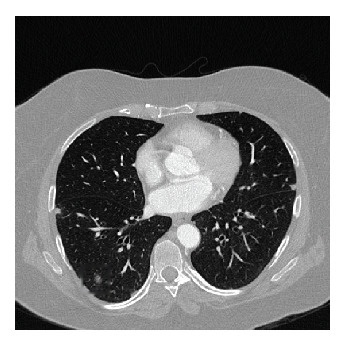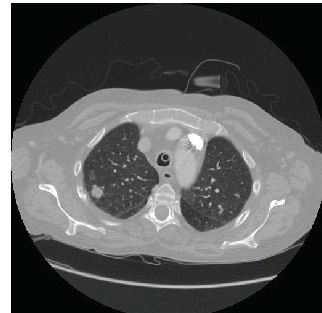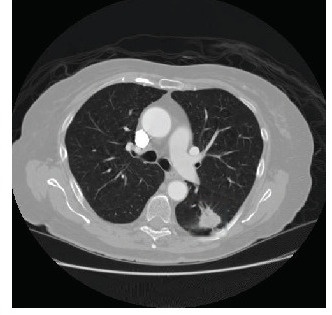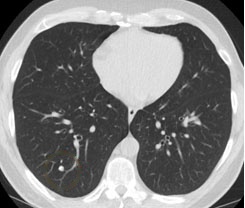
3D Image Processing
Utilizes advanced techniques to handle 3D volumetric data obtained from medical imaging (e.g., CT scans), allowing for comprehensive analysis of complex lung structures and nodules.

Nodule Segmentation with 3D U-Net
Employs a 3D U-Net architecture, an extension of the traditional U-Net designed for biomedical image segmentation, to accurately delineate the boundaries of lung nodules. This deep learning model is specifically tailored for 3D data, capturing spatial hierarchies and contextual information in all three dimensions.
Deep Learning-Based Classification
Implements a 3D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to classify segmented nodules into normal or abnormal categories. This model leverages 3D convolutional layers to extract volumetric features that are critical for understanding the morphological characteristics of lung nodules.
Automated Feature Extraction
The system automatically extracts relevant features from 3D lung images, such as shape, texture, and intensity characteristics of nodules, without the need for manual feature engineering, leveraging the inherent capability of deep learning models.
Multi-Scale Analysis
Incorporates multi-scale analysis to capture features at various resolutions and sizes, ensuring that both small and large nodules are accurately detected and classified, enhancing the model's sensitivity and specificity.

Clinical Integration Potential
Designed with a focus on clinical applicability, the project aims to integrate seamlessly into existing medical imaging workflows, providing radiologists with a powerful tool to enhance diagnostic accuracy and efficiency in lung cancer screening and diagnosis.